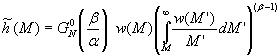
full page for printing
back to case studies
Objective: Calculation of the
Molecular Weight Distribution (MWD) from dynamic mechanical data G', G"(w).
The module is intended to estimate the Molecular Weight Distribution, w(M), of a polymer melt from dynamic mechanical data in the terminal zone. The MWD dependent kernel introduced by Timm et al. is used to correlate MWDs to the linear viscoelastic behavior. In particular the relation between the relaxation time spectrum h(l) and w is considered
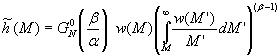
where a »
3.4 is the scaling exponent, and the constant k is a material parameter
in the scaling relation for the relaxation time as a function of the molecular
weight ![]() and
and ![]() .
.
The ill-posed problem of the inversion is solved by constraining the MWD function to a Generalized Exponential (GEX) function.
To begin with the MWD determination,
we open the IRIS data file (w,G',G")
of the linear polymer, see below:
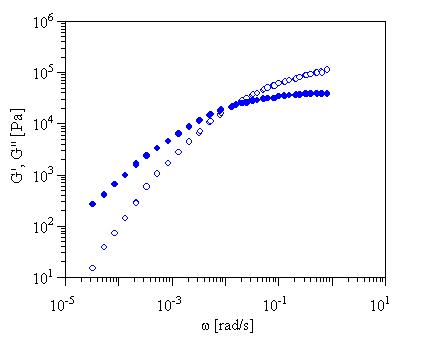
The program asks for a modulus value
(optional) and then calculated MWD. The results looks like this:
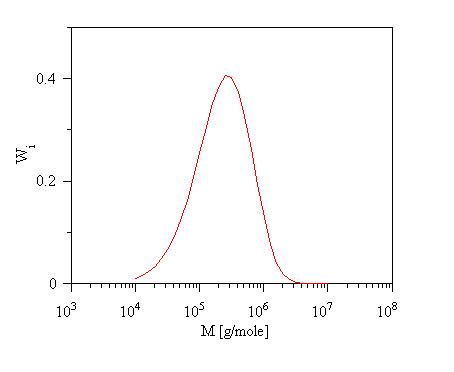
Calculated generalized
exponential distribution
Reference: Cocchini F,
Nobile MR (2003) Rheol Acta 42:232
**** Input Parameters
****
mixing rule exponent
(beta) : 2.00 [-]
scaling law exponent
(alfa) : 3.40 [-]
scaling law constant
(k) : 8.00e-018 [s/(g/mole)^alpha]
Plateau modulus
(GN0) : 2.00e+005 [Pa]
MWD distribution : GEX
Rouse start-up
threshold frequency : 8.10e-001 [rad/s]
**** Output Parameters
****
Standard deviation on
fit : 3.91e+000 [%]
Plateau modulus
(GN0) : 2.00e+005 [Pa]
Zero-shear viscosity
(eta0) : 8.40e+006 [Pa s]
Steady-state
compliance (je0) : 2.50e-004 [1/Pa]
GEX a constant : 1.1210e+000 [-]
GEX b constant : 5.1180e-001 [-]
GEX M0 constant : 1.7000e+004 [g/mole]
Average Mn
: 1.1182e+005 [g/mole]
Average Mw
: 3.3459e+005 [g/mole]
Average Mz
: 6.7015e+005 [g/mole]
Mw/Mn
: 2.9921e+000 [-]
Mz/Mn
: 5.9930e+000 [-]
Mz/Mw : 2.0029e+000 [-]
MOLECULAR WEIGHT
DISTRIBUTION
No. M w(M)
[g/mole] [-]
1 1.000e+004 1.076e-002
2 1.259e+004 1.593e-002
3 1.585e+004 2.333e-002
4 1.995e+004 3.369e-002
5 2.512e+004 4.793e-002
6 3.162e+004 6.704e-002
7 3.981e+004 9.199e-002
8 5.012e+004 1.236e-001
9 6.310e+004 1.620e-001
10 7.943e+004 2.067e-001
11 1.000e+005 2.557e-001
12 1.259e+005 3.057e-001
13 1.585e+005 3.516e-001
14 1.995e+005 3.871e-001
15 2.512e+005 4.058e-001
16 3.162e+005 4.026e-001
17 3.981e+005 3.753e-001
18 5.012e+005 3.264e-001
19 6.310e+005 2.623e-001
20 7.943e+005 1.930e-001
21 1.000e+006 1.286e-001
22 1.259e+006 7.658e-002
23 1.585e+006 4.022e-002
24 1.995e+006 1.833e-002
25 2.512e+006 7.125e-003
26 3.162e+006 2.315e-003
27 3.981e+006 6.148e-004
28 5.012e+006 1.301e-004
29 6.310e+006 2.133e-005
30 7.943e+006 2.625e-006
31 1.000e+007 2.337e-007
GENERALIZED EXPONENTIAL DISTRIBUTION
References
Nobile MR, Cocchini F (2001) Evaluation of molecular weight distribution from
dynamic moduli. Rheol Acta 40:111-119
Cocchini F, Nobile MR (2003) Constrained inversion of rheological data to
molecular weight distribution for polymer melts. Rheol Acta 42:232-242
Thimm W, Friedrich C, Marth M (1999) An analytical relation between relaxation time spectrum and molecular weight distribution. J Rheol 43: 1663-1672